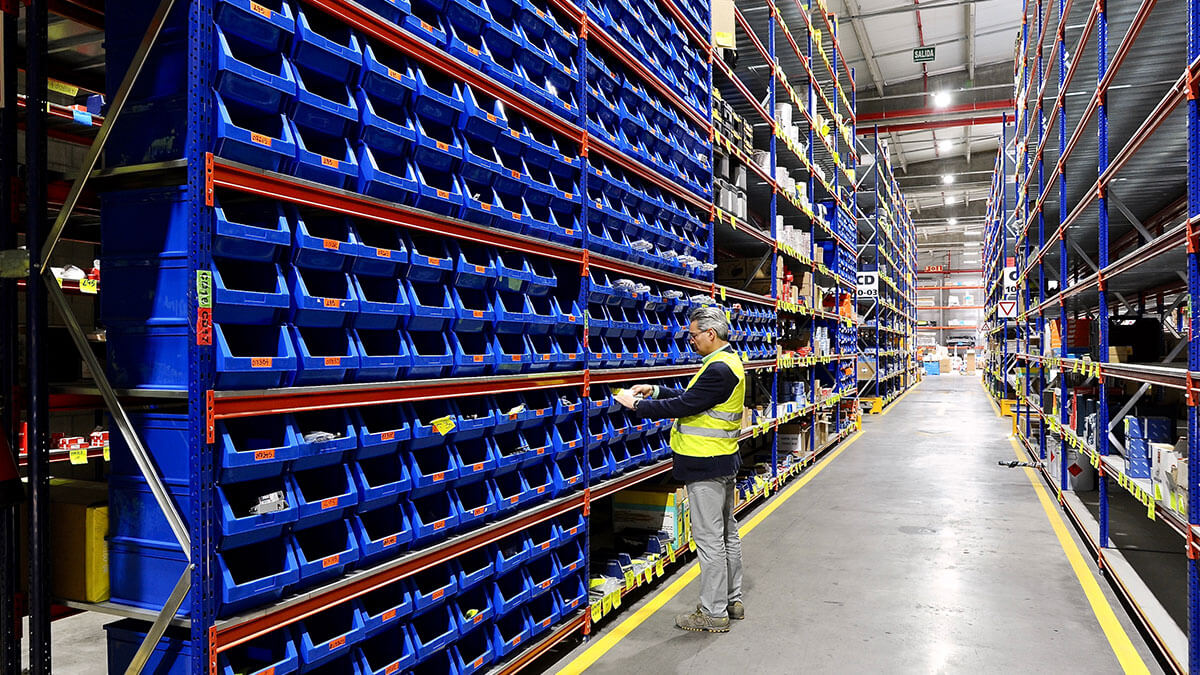
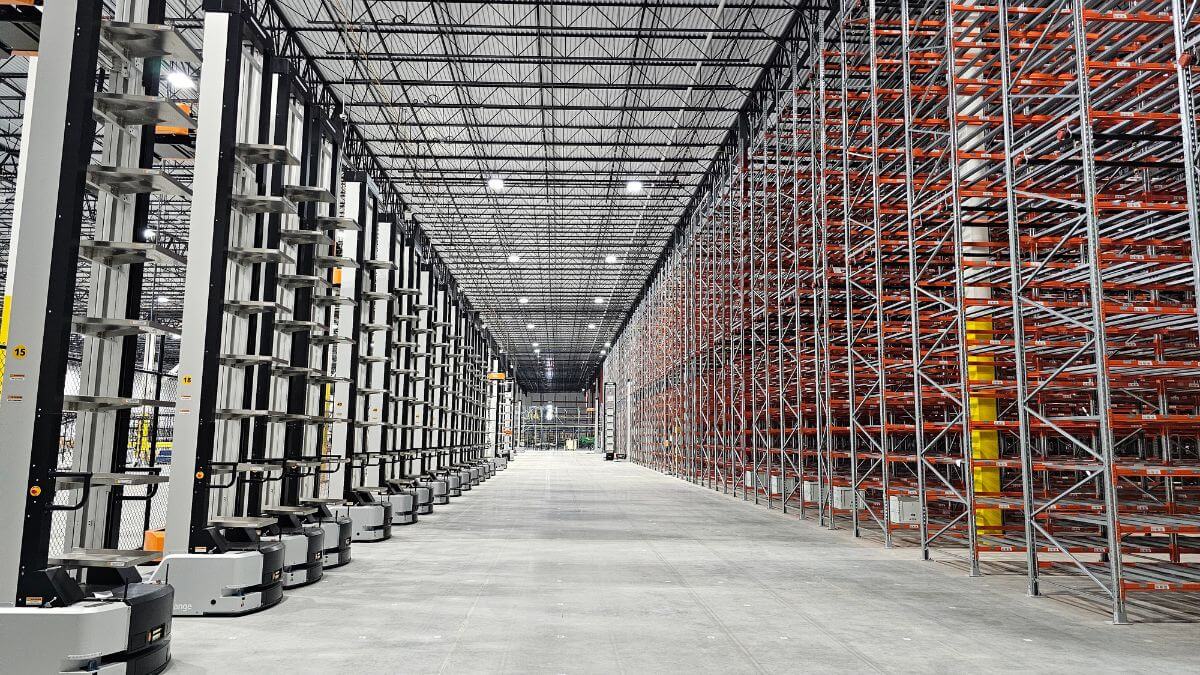
In logistics warehouses there are two main different types of storage, firstly, storage for heavy loads generally using pallet racking solutions and, secondly, manual storage or picking solutions for lighter loads.
We will look at the concept of picking in logistics, the types of picking and their phases, as well as the main solutions that enable this type of storage.
What is picking in logistics?
In logistics, picking is understood as the organisation and preparation in the supply chain of a product or order.
It represents a significant part of the cost in logistics operations and processes, as it involves several actions such as order fulfilment, including packaging and labelling, control and movements of the order, etc.
It is important to consider the quality of this process, as the greater its optimisation, the faster the preparation and results, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and fewer errors and lower costs.
Both the reverse logistics costs and opportunity costs will increase if the products in the process are defective or contain any errors and damage. This can arise if the company does not have good strategic planning or lacks manpower. This problem will result in delayed order delivery times and reduced customer satisfaction.
Minimising the time of these operations and performing them correctly has led to companies establishing complex and effective picking solutions.
Picking phases in a warehouse or logistics centre
It was commented above how picking contains several actions, which are summarised below:
Preparation
This is the pre-planning where all the order data is collected and the resources are assigned, for example, the delivery notes, location and the segmentation of these. The elements or resources used for this preparation will be the different types of pallets, forklifts, equipment, etc.
Routes
Operators move around the warehouse aisles to locate the orders or products. This phase can take the most amount of time. The routes they take will be as follows: from their workstation to the places where each product or order is located, and from the location of the last order to the order preparation area.
Removal
This phase will be faster and more agile if the products are classified by labels, well located and easy to collect. After they have been located, the quantity requested will be taken and placed on selected transport. It will be necessary to know if ladders, forklifts, etc. will be needed.
Verification
This is the final phase where the order is completed. It will be checked firstly to see that everything is as requested. This is also divided into phases, starting with preparing the order to ensure it is secure, packing and weighing it, attaching the label with the corresponding data and finally transferring the package to the shipment area taking into account the different carriers and destinations.

Types of picking
The types of picking can be classified into three categories:
Operator to product picking
This will be the person responsible for fulfilling the order, in this case, the operator, who will move around the warehouse to look for the product. It is classified into four groups:
- Floor level picking: the products are located on pallets on the floor, providing faster order preparation, as no other type of machinery is required for its collection and the operator is able to see at all times the product to avoid any errors.
- Picking at low levels: this is the level above floor level and cannot exceed the operator’s shoulder height, as the operator will move around the warehouse on foot without any type of machine to collect the product. This level must also be easy to access and ensure less time is wasted.
- Picking at intermediate levels: this level ranges from the operator’s shoulder height to above, without exceeding four metres in height. Goods located at this height will be the least demanded, as they will need machinery and time to access them.
- Picking at high levels: at these heights, spaces can be fully exploited vertically, up to the maximum height of the racking. To access them, both specialised machinery and time is needed. As with the intermediate levels, here the goods least requested will be placed and organised by spaces, batches, aisles, etc.
Product to operator picking
Here it is a machine that performs the picking process. The operator won’t have to move around the warehouse and will only have to wait for the machine to bring them the order. The machine is programmed with different software systems that carries out all the tasks from location to collection and delivery to the operator.
Mixed picking: combination of both types
This type of picking is a combination of both of the above-mentioned types. The warehouse will be automated with machines, but the operator will also be involved in the process. It is used for different types of picking depending on the goods, whether large, small, easy or difficult to access.
Keys for optimising the picking or order preparation process
Each warehouse will require different picking processes, but there are five keys to help optimise the processes regardless of the size or type of warehouse.
- Firstly, the goods must be correctly located with their corresponding references, and without mixing them with other different references. This will ensure less time wasted for the operator and the streamlining of the whole process.
- As far as possible, it will be more convenient and faster working closer to floor level as the goods will be within reach of the operator without the need for machines. However, when there are too many products and more storage space is needed, these products will need to be placed vertically with optimised and well-organised systems, placing the most demanded products lower down and the least demanded ones higher up, using the right machinery at all times.
- So that the operator or the machine working on the process does not waste time travelling very long distances, the space should be small and easy to access.
- The routes that the operators or machines take need to be fully exploited, so when they move around the warehouse they must collect the orders in batches and not individually.
- There must be no intermediary between the picking of the order in the warehouse and its delivery to the end customer.
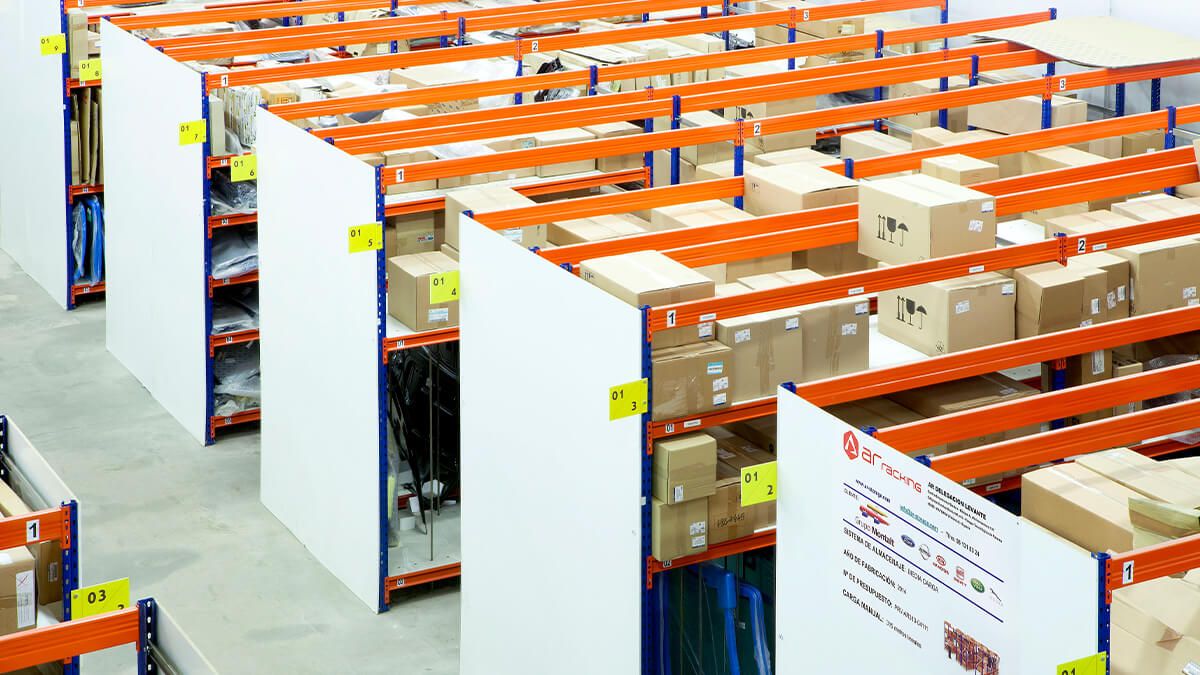

Picking storage systems
Considering the different types of picking and its keys, we outline below some of the most common and useful picking storage systems. There are different types of racking that provide manual picking storage solutions, from more simple solutions such as Longspan Shelving or AR Light Shelving, to more complex systems such as Multi-tier Racking or Carton Flow Rack Systems.
The systems adapt to the needs of each type of customer, and will be as follows:
Longspan Shelving Systems
Longspan shelving systems facilitate the manual storage of medium or small loads. It is a highly versatile and conventional picking system. In addition to being very simple to assemble, it is easy to adapt to different sizes or volumes of goods.
Multi-tier Racking
It is a storage system at height that enables space optimisation, creating different levels accessed via ladders. It is designed to store medium or light loads and is an ideal solution for picking warehouses with reduced floorspace, but with the possibility of growth at height.
Carton Flow Rack Systems
Carton Flow Rack Systems are designed to store medium and light loads using the FIFO warehouse management method. As with the live pallet racking system, the unit loads move through the racking on roller beds.
It is a compact storage system, resulting in a significant saving in available space and it also reduces the distances covered by the operator in the warehouse. It is a system that is regularly used as a complement to other storage systems, such as the adjustable pallet racking system, with live pallet racking being installed on its lower levels.
AR light shelving
It is a similar system to longspan shelving, but designed for lighter loads, with the possibility of installation both in warehouses and in offices.
It is very simple to assemble and adaptable to a variety of goods thanks to the accessories that can be added to it.