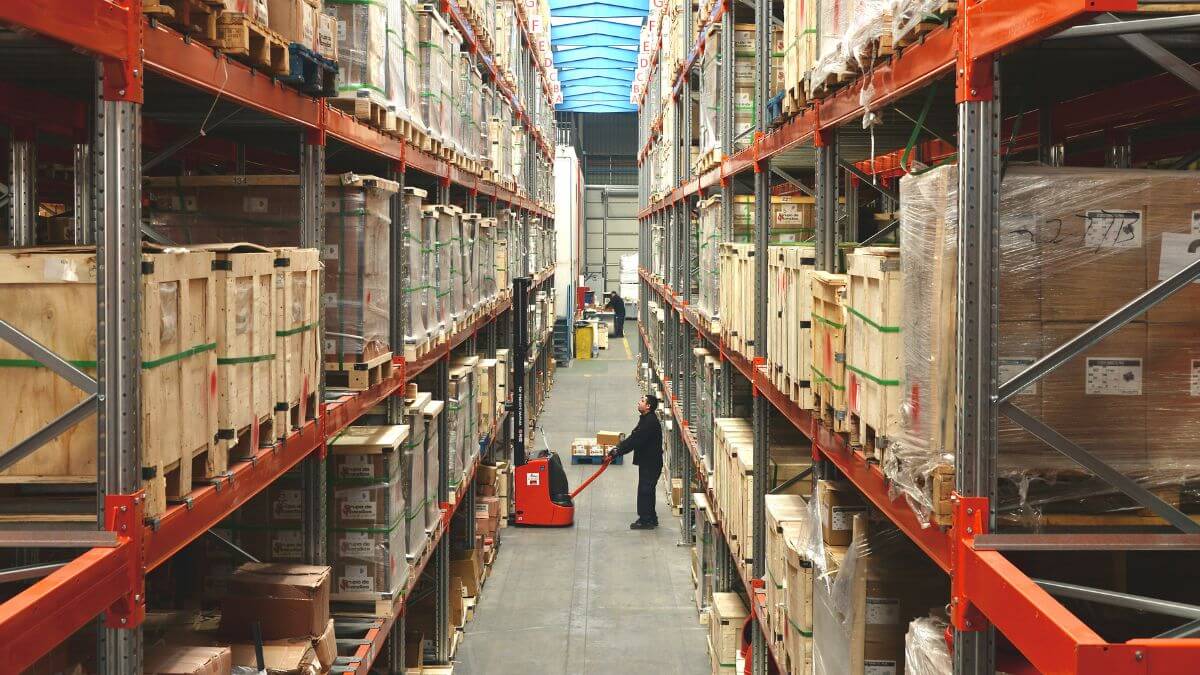
The warehouse is the space where goods are stored after their production until their delivery to the customer. It is vital to maintain a constant and up-to-date flow of goods and information to ensure the proper functioning of the supply chain, with this being one of the main warehouse tasks, among others.
What is a logistics warehouse?
A logistics warehouse is a facility specifically designed for the receipt, storage and distribution of products within a supply chain.
Its main task is to facilitate efficient inventory management and to ensure that the products are available at the right time and place to meet customer demand.
Main functions of the logistics warehouse
With this important role within the supply chain, we can list the functions of the logistics warehouse as follows:
- Receipt of goods: Involves verifying, inspecting and recording the entry of products in the warehouse, ensuring that they comply with the specified quantities and quality.
- Storage: Organises and stores the products safely and efficiently, optimising the space to facilitate product access and reduce handling times.
- Inventory control: Maintains an accurate stock record, making it possible to anticipate supply needs and avoid any stockout or overstock.
- Order preparation or picking: Selects and groups the products requested by the customers, preparing the orders quickly and accurately for shipment.
- Packaging: Protects and labels the products for their transport, ensuring that they arrive in optimum conditions and are easily identifiable.
- Shipment and dispatch: Organises the orders by routes and delivery dates, coordinating their issue for effective and timely distribution.
- Management of returns: Manages returned goods, verifying their status and determining whether they can be returned to inventory or whether they require special provision.
These functions work together to ensure that the logistics warehouse operates in an organised way and meets supply chain demands.

Logistics warehouse areas
Considering the above functions, the warehouse is organised into different areas to respond to these needs and thus optimise the flow of goods and ensure an efficient product reception, storage, preparation and dispatch process.
Goods Receiving Area
Here all the goods that arrive at the warehouse are received and checked. Quality control is performed, quantities are checked and the goods are recorded in the system for their subsequent storage. This area is crucial for ensuring that all the products are in good condition and enter the warehouse in the correct quantity.
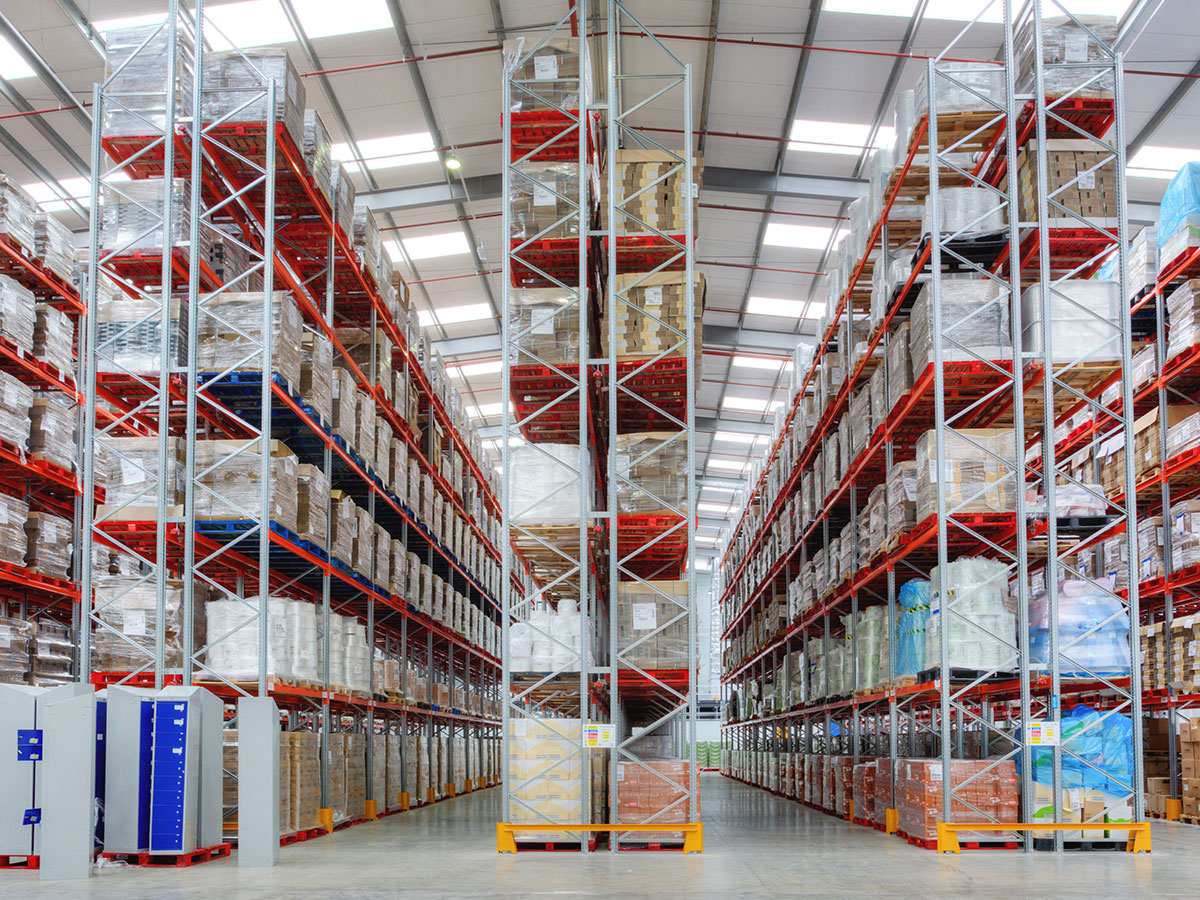
Storage Area
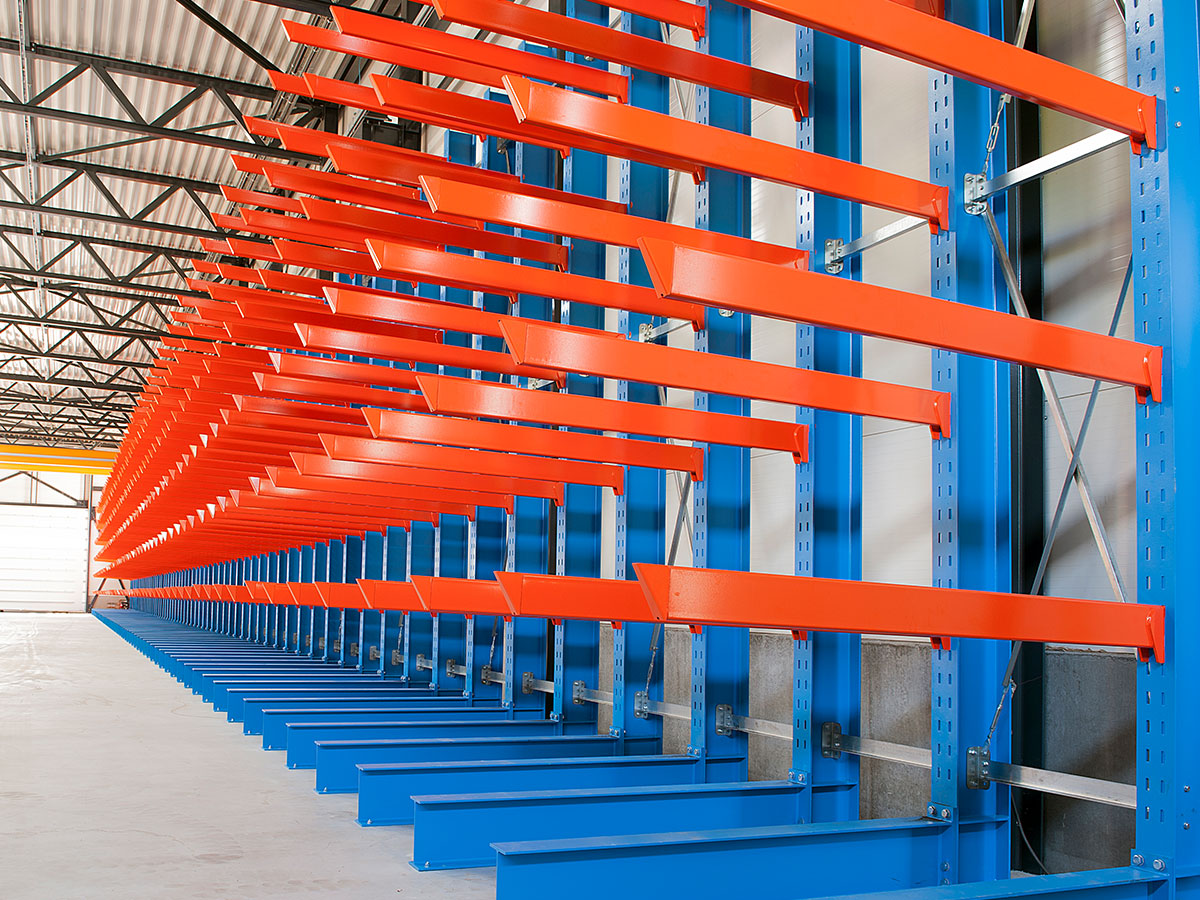
The products are stored safely and in an organised way in this area. Storage can be arranged on racking for easily accessible products or in blocks for goods that can be stacked without risk. Special racking can also be used, such as live storage or drive-in, to optimise the use of space according to the product characteristics.
Order Preparation Area (picking)
Here products requested by customers are selected, grouping them for their shipment. Depending on the needs, picking can be by product, order or zones, allowing pickers to pick the products in specific areas. This area is essential for ensuring that orders are prepared quickly and accurately.
Consolidation Area
Picked products are grouped together in this area before their packaging and shipment. This step ensures the items are gathered in a single order so that they are ready for packaging, avoiding errors and facilitating the shipment process.
Packaging Area
Here the orders are packaged and labelled to ensure their protection during transport and to facilitate their identification. In this area suitable packaging such as bubble wrap or film is used and the shipping labels and corresponding documentation are placed to ensure the products reach the end customer in perfect condition.
Shipment or Dispatch Area
In this area the orders are organised and prepared for their transport and final delivery to the customer. The products are grouped according to the delivery routes and loaded onto the transport vehicles, guaranteeing an orderly and efficient issue process.
Returns Area
This is where goods returned by customers, whether due to defects or order errors, are managed. Returned products are inspected here, their condition is determined, and whenever possible, they are returned to inventory or assigned for provision, enabling proper control of returns.
Storage Area for Auxiliary Materials
This area is for materials used in the warehouse, such as tools, packaging equipment and other necessary supplies. This enables easy access to these materials when they are required in other areas of the warehouse.
Loading and Unloading Area
This is the area for moving goods from and to the transport vehicles. Specialised equipment is used, such as forklifts, to streamline inflows and outflows, improving the flow of goods in the warehouse.
Quality Control Area
Here it is checked that the products meet the required quality standards before being stored or shipped to the customer. This control makes it possible to identify and resolve any quality issue, ensuring customer satisfaction and maintaining product standards.
These areas in a logistics warehouse facilitate organisation and ensure that each product is processed efficiently and accurately, from receipt through to customer delivery.

Importance of the logistics warehouse in the supply chain
The importance of the logistics warehouse in the supply chain is vital to ensure an efficient flow of goods and customer satisfaction. Some of the main aspects of its role are detailed below:
Inventory optimisation
Logistics warehouses allow companies to manage their inventory more effectively. By storing products strategically, companies can reduce the risk of overstock and stockout, which helps to maintain an optimum balance between supply and demand.
Improved operations
A well-organised and equipped warehouse with suitable technology facilitates the receipt, storage and distribution of products. The implementation of suitable storage systems and the possibility of automating processes can reduce handling times, improve picking accuracy and expedite shipments.
Optimisation of costs
Effective storage helps minimise operating costs, such as transportation and inventory management-related costs.
A warehouse that optimises space and improves processes can significantly help reduce general supply chain costs.
Risk management
A well-managed warehouse helps companies to mitigate supply chain-related risks.
This includes handling disruptions, such as supplier issues or changes in demand. Having adequate inventory and an efficient storage system allows companies to adapt more easily to unforeseen situations.
Centralisation of the logistics process
Warehouses act as distribution centres where logistics operations are centralised. This enables better coordination between suppliers, carriers and customers, which is essential for an efficient supply chain.
Facilitation of reverse logistics
Warehouses are also vital for managing reverse logistics, i.e., the process of returning products. A well-designed logistics system allows an efficient product returns process, which not only reduces costs, but also improves customer satisfaction.
Types of logistics warehouses
We can differentiate between logistics warehouses according to several categories and types, which we outline in this other blog on types of warehouses, and which we set out below:
By their enclosure
- Indoor or covered warehouses
- Outdoor or open-air warehouses
By type of product or goods stored
- Finished goods warehouse
- Semi-finished goods or work-in-progress warehouse
- Raw material warehouse
- Packaging and containers warehouse
- Auxiliary materials warehouse
- Spare parts warehouse
By degree of automation
- Adjustable pallet racking warehouses
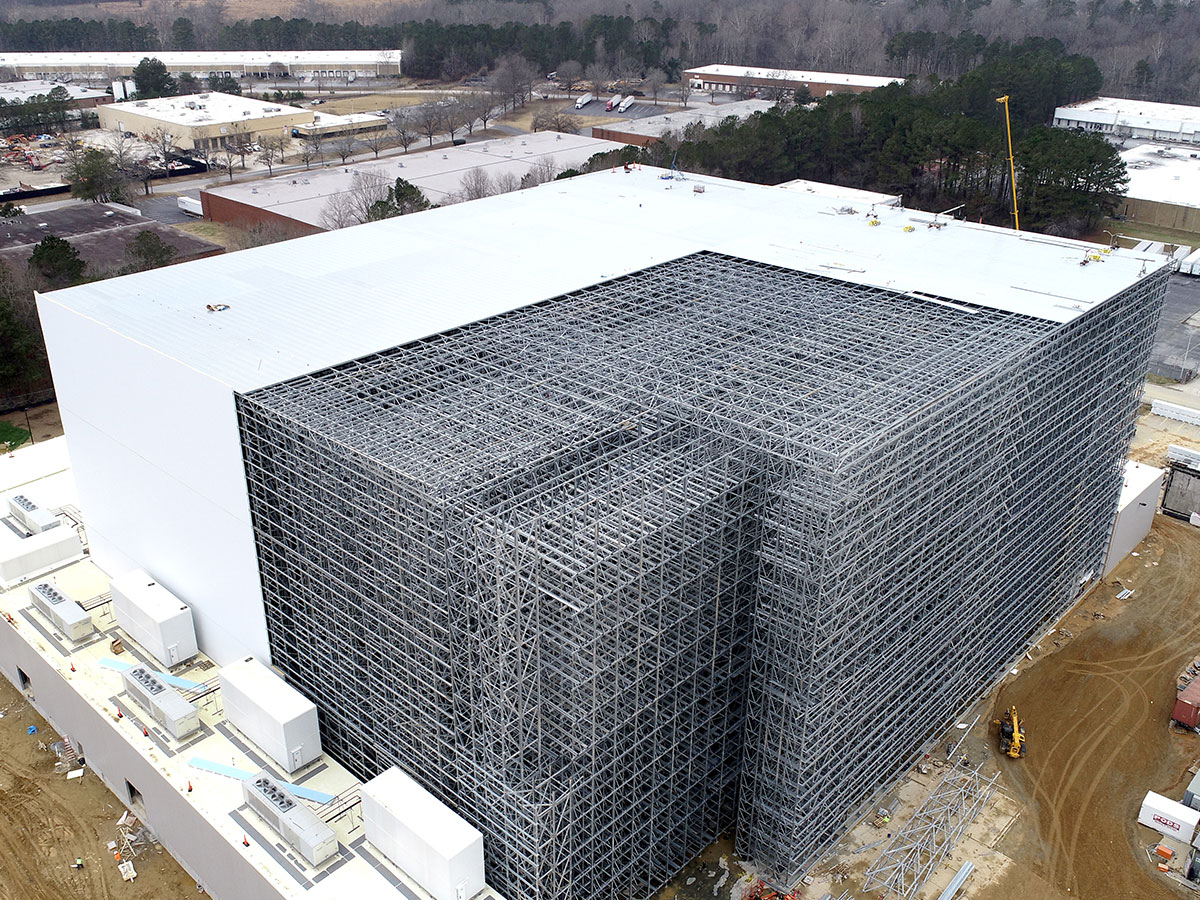
- Automated warehouses
By their logistics function
- Central warehouses
- Regional or distribution warehouses
- Supply or production warehouses
- Transit warehouses
- Temporary storage warehouses
- Picking warehouses
- Consolidation warehouses

How can the operation of a logistics warehouse be optimised?
The relationship between the warehouse and logistics is key to the success of the activity. It is therefore important to implement measures to improve the overall operation of the warehouse logistics. Some of these measures are as follows:
- Adapt the logistics strategy to the dimensions of the warehouse. The needs will be different in a large distribution centre compared to a small warehouse.
- Optimise the work environment to reduce transfer and movement times within the warehouse.
- Invest in quality equipment to improve the efficiency and safety of operations.
- Establish clear, well-defined protocols for ordinary activities and for exceptional situations that may arise.
- Segment the storage areas, reserving an area for fast-moving items and another for the slowest moving inventory.
- Train workers in different picking methods to streamline the process.
- Minimise product storage time and optimise distribution logistics, whenever possible, to reduce costs and delivery times.
- Re-engineer internal warehouse and logistics processes to improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Perform quality controls to prevent errors and ensure customer satisfaction.
The warehouse and logistics are elements that must work together in a coordinated way to achieve maximum efficiency.
Effective coordination between both guarantees the optimisation of warehouse logistics and streamlines the entire logistics process. This not only significantly reduces operating costs, but also ensures the delivery of a quality service to customers.
Correct synchronisation between storage, inventory management, transport and distribution is essential to achieve these objectives and maintain market competitiveness.
At AR Racking we help you to equip your new warehouse or already existing facilities with the appropriate storage system to ensure the proper functioning of the supply chain. Contact us and our team of experts will advise you on the best storage solutions.