In the warehouse logistics and management sector, efficiency and accuracy are crucial to meet current market demands. The need to handle high order volumes means companies are continuously looking for innovative methods to optimise their operations. One of these is Pick to Cart, recognised for its effectiveness for improving product picking in warehouses.
What is “Pick to Cart”?
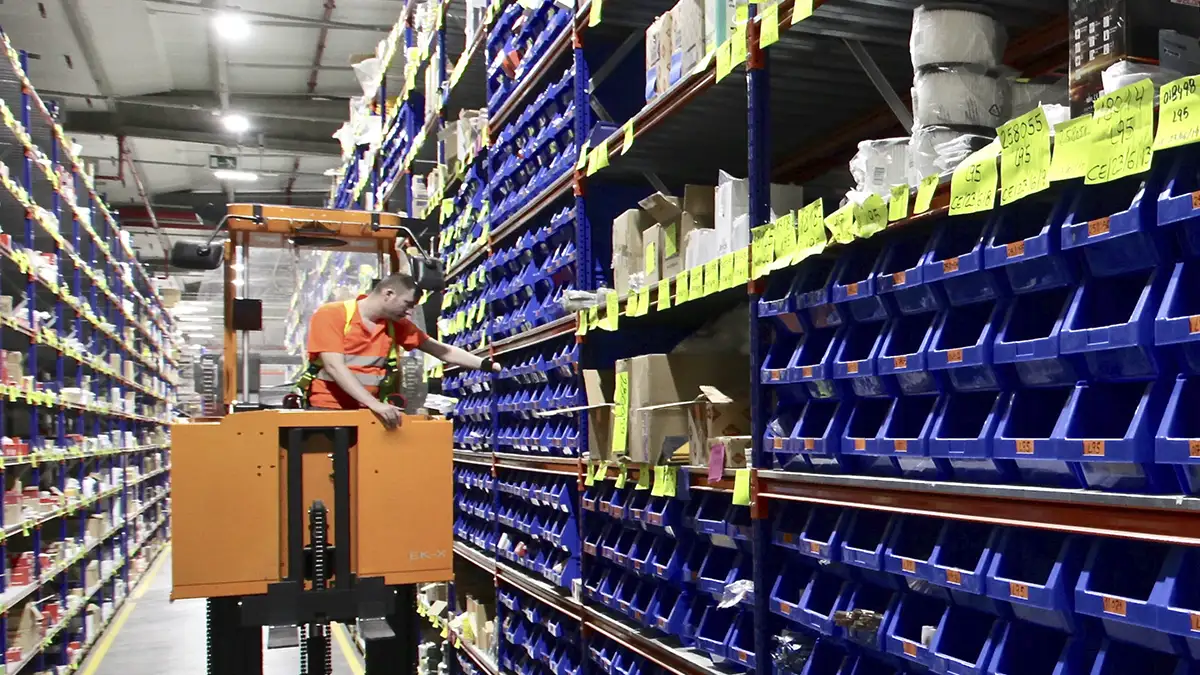
Pick to Cart is a warehouse management technique that optimises order preparation through the use of picking carts. In this system, warehouse workers pick products requested directly in these carts, allowing a more efficient and accurate picking process. This method is particularly advantageous in sectors such as e-commerce and retail, where speed and accuracy are essential to meet customer expectations.
How does the Pick to Cart system work?
To better understand how the Pick to Cart system works, it is useful to break down the process into clear and organised steps. Each stage of the process, from receiving the order through to customer delivery, is briefly outlined below:
Order Receipt:
If a customer makes an online purchase, the order is recorded automatically in the WMS system. This system centralises all the information, including customer details, products requested, quantities and any special instruction. This ensures that the order is ready to be processed efficiently and error-free.
Example: A customer purchases a book and a shirt in an online store. The order is recorded in the WMS with all the necessary details for its processing.
Task Assignment:
The WMS system analyses orders and assigns specific tasks to warehouse workers. It uses algorithms to optimise task distribution, ensuring that each worker has a balanced workload and that the products are picked efficiently.
Example: The system assigns a worker the task of picking several items from different orders, such as toys and stationery, from different warehouse sections.
Cart Preparation:
Before starting to pick products, the worker prepares a picking cart. This cart is equipped with labelled containers that help organise the products according to the orders. This facilitates picking and reduces the risk of errors.
Example: The worker places labelled containers in the cart to organise the products that are going to be picked, making sure that each container corresponds to a specific order.
Product Picking:
The worker follows an optimised route within the warehouse, designed by the WMS to minimise the time and distance covered. As each product is picked, the worker scans it with a hand-held device to confirm its picking and update the inventory in real-time.
Example: The worker follows an efficient route within the warehouse and scans each product as he/she picks them from the racks, ensuring that it matches the order.
Verification:
Once all the products have been picked, a final verification is carried out. The worker scans each product once again to ensure that all the items match the order details. This helps prevent errors and ensures that the customer receives exactly what it ordered.
Example: The worker scans each product picked to ensure that it matches the items requested in the order, verifying quantities and specifications.
Packaging:
After verification, the products are carefully packaged for shipment. Suitable packaging materials are used to protect the items during transport. Each package is labelled with the customer’s shipping information and any special instruction.
Example: The products are carefully placed in boxes, sealed and labelled with shipping information, ensuring that they are protected and ready for transport.

Application cases
Pick to Cart has been successfully implemented in several sectors, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness:
E-Commerce:
Companies such as Amazon use this system to manage large volumes of orders efficiently, enabling the highly accurate processing of thousands of orders per day.
Retail:
Supermarkets and convenience stores use Pick to Cart to streamline product replenishment on industrial racking, improving product availability for customers and maintaining optimal supply logistics.
Distribution Centres:
Logistics and distribution companies, such as DHL, use this method to optimise order preparation and dispatch, improving the efficiency of their global operations.
Ideal Storage Systems for Pick-to-Cart Warehouse Management
The Pick-to-Cart warehouse management system focuses on order preparation by having operators move around with carts, collecting products from different locations within the warehouse. This approach is particularly useful in e-commerce, retail, or situations where the order volume is high but individual order sizes are small. To optimize this technique, it is crucial to implement storage systems and industrial shelving designed to maximize accessibility, efficiency, and accuracy.
Longspan Shelving
An ideal solution is the manual picking shelving system. These shelves are designed to provide quick and direct access to products, facilitating the work of operators. They typically feature adjustable levels that adapt to the dimensions of the items, allowing for efficient organization and optimal space utilization.
Live Storage for Picking
Additionally, dynamic picking shelving is highly recommended. These structures incorporate rollers or inclined surfaces that enable products to move automatically to the front, reducing search times and improving accessibility. This system is particularly effective in high-turnover operations and for handling lightweight products.
It is essential for the storage system design to be flexible and aligned with the Pick-to-Cart workflow. The incorporation of clear signage and technological tools such as voice-picking systems or scanners can further enhance the efficiency of shelving solutions.
With the right configuration, warehouses implementing Pick-to-Cart can achieve the perfect balance between speed, organization, and ergonomics in their logistics operations.
Types and choice of Pick to Cart carts
There are different types of picking carts, each one designed to meet specific warehouse needs:
Manual Carts:
Simple and economic, ideal for small warehouses. These carts are usually equipped with adjustable shelves and wheels that facilitate movement.
Automated Carts:
Equipped with scanning and navigation technology, suitable for large distribution centres. Some automated carts can follow pre-determined routes and stop automatically at picking locations.
Carts with Adjustable Shelves:
They allow the picking of products of different sizes and shapes, useful in warehouses that handle a variety of products.
Carts with Weighing Systems:
They incorporate scales to check the weight of the picked products, ensuring accuracy, particularly in industries where product weight is critical, such as in the food sector.
Roll Containers:
They are metal carts with mesh panels that enable the safe transport of packages, often with horizontal shelves to increase their capacity.
Pick-to-Box Carts:
Designed so that products are placed directly in shipping boxes during picking.
Management software
The efficiency of the Pick to Cart system depends to a large extent on the technology used; management software is key to success as it provides tools to coordinate and optimise operations. Some important features include:
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):
They coordinate and optimise picking operations, assigning tasks to workers according to product location and order priority.
Scanning Technology:
It uses barcodes or RFID to ensure picking accuracy, allowing workers to scan each item picked and check it against the order.
Integration with ERP:
It enables comprehensive management of inventories and orders, automatically updating inventory management in real time as the products are picked.
Data Analysis:
It provides reports and analysis to continuously improve the processes, identifying bottlenecks and suggesting improvements.

Special considerations
To maximise Pick to Cart benefits, it is important to consider several additional factors:
Staff Training:
It is essential that workers are well trained in using the carts and software. Adequate training can reduce errors and increase efficiency.
Warehouse Design:
Efficient warehouse design can maximise Pick to Cart benefits. Position fast-moving items near warehouse areas that are strategic for reducing time.
Equipment Maintenance:
Ensuring that the carts and software work properly is essential to avoid disruptions. For instance, a regular maintenance programme can prevent failures and extend the useful life of the equipment.
Conclusion
Pick to Cart is an effective strategy to improve order preparation efficiency and accuracy. With the right combination of picking carts, management software and an optimised warehouse design, companies can achieve a more streamlined and profitable logistics operation; however, the volume and movement of items in the warehouse needs to be analysed.
If you are looking to improve the logistics efficiency of your warehouse with high-quality storage, at AR Racking we are fully able to assist you. Contact our team of experts to receive a detailed assessment and recommendations tailored to your company's unique requirements.