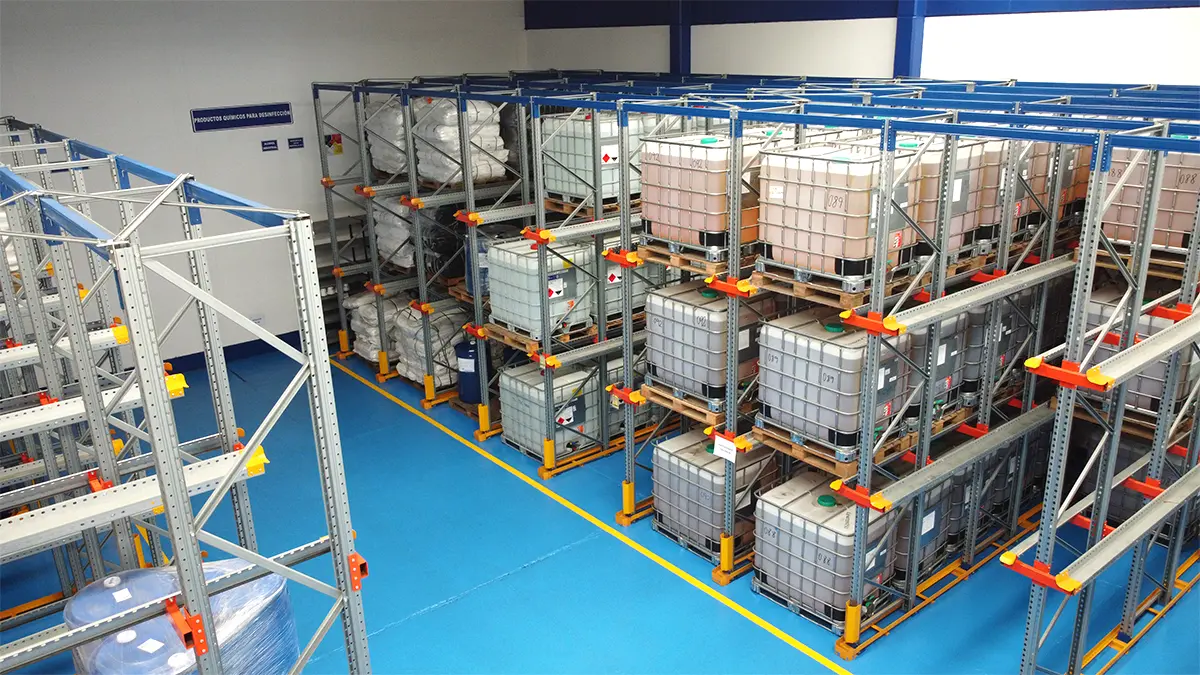
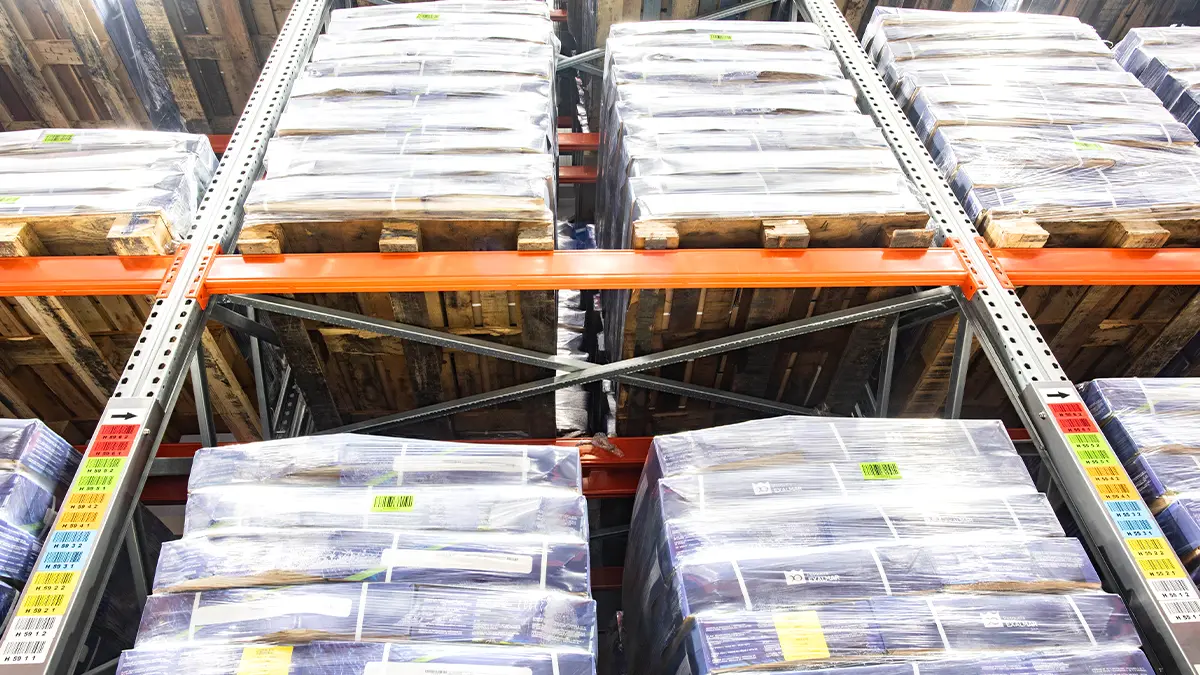
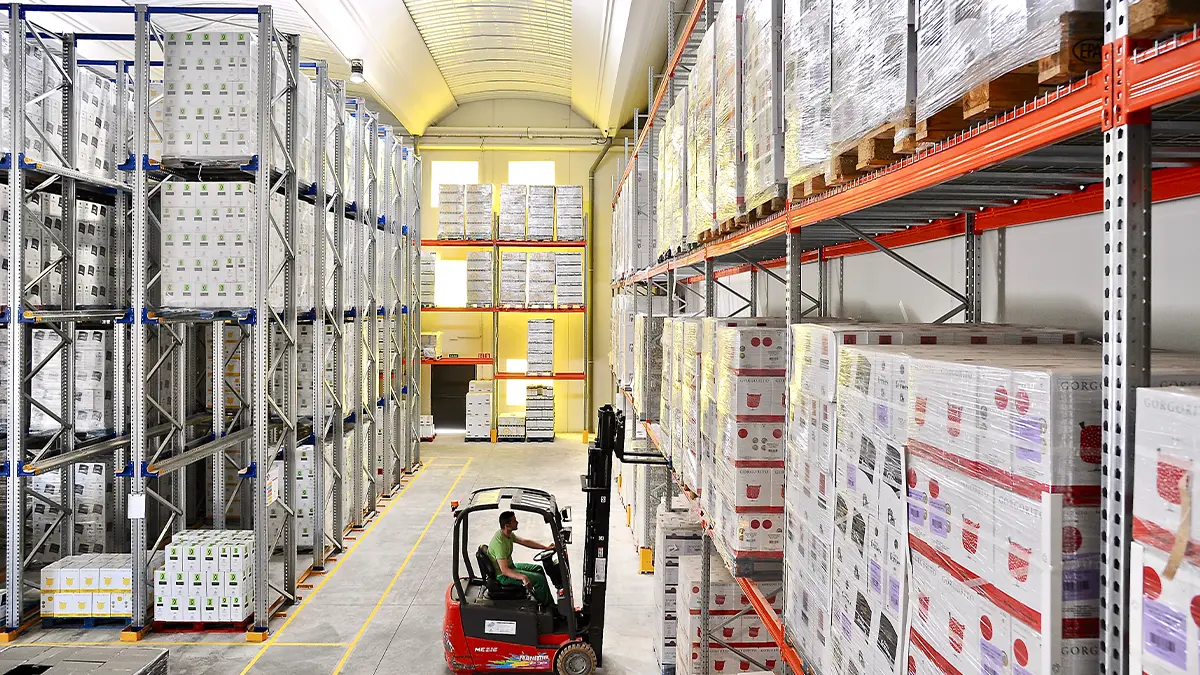
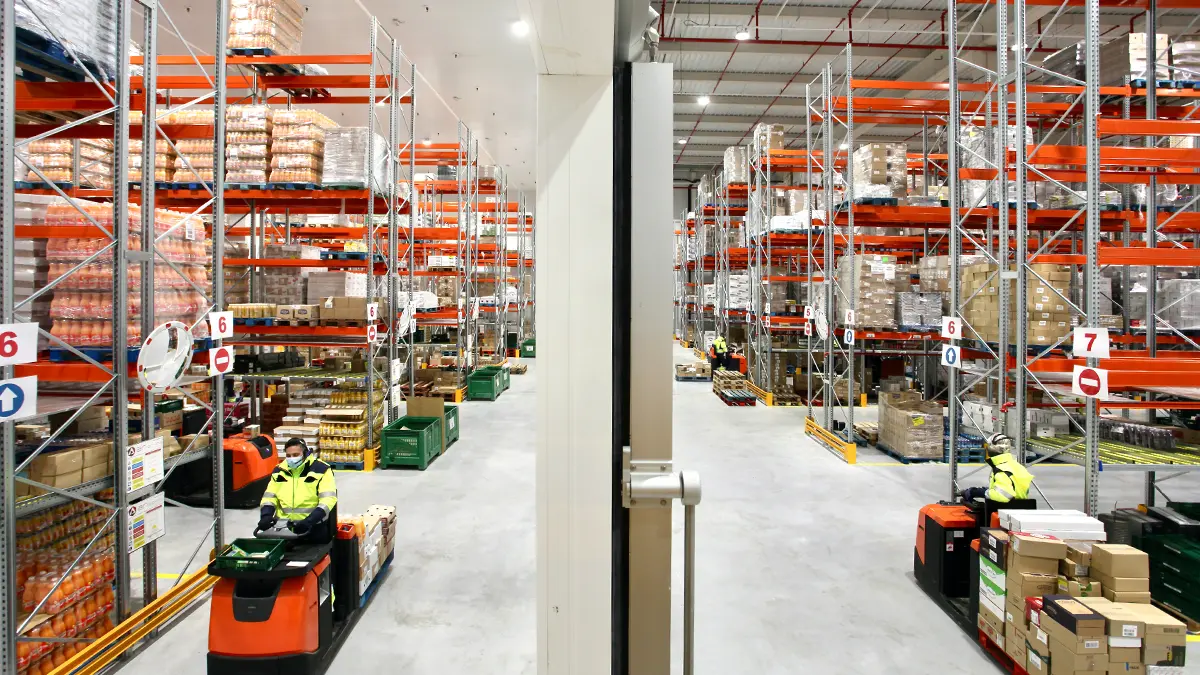
Safe storage of hazardous materials is crucial to protect human health, the environment, and facilities. These materials, which include chemicals, industrial waste, and other hazardous products, can cause significant damage if not handled properly.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on the most important aspects to consider when storing such goods.
Classification of hazardous materials
Hazardous materials are classified into several categories based on their characteristics and the risks they present. This classification is essential to ensure their safe handling and storage. Below are the main classes of hazardous substances or materials:
Explosives
Description: Explosives are substances that can cause explosions due to rapid chemical reactions that release gases and heat. These materials are extremely dangerous and require careful handling.
Subdivisions:
- Cl.1.1: Materials with a mass explosion hazard.
- Cl.1.2: Materials with a projection hazard.
- Cl.1.3: Materials with a fire and minor blast hazard.
- Cl.1.4: Materials with a minimal hazard.
- Cl.1.5: Very insensitive explosive agents.
- Cl.1.6: Extremely insensitive articles.
Gases
Gases can be flammable, non-flammable, toxic, or corrosive. They are stored under pressure, which adds an additional risk in case of leaks or container ruptures.
Subdivisions:
- Cl.2.1: Flammable gases.
- Cl.2.2: Non-flammable, non-toxic gases.
- Cl.2.3: Toxic gases.
Flammable liquids
Flammable liquids are those that can easily ignite at relatively low temperatures. They include fuels such as gasoline and alcohol.
Examples: Gasoline, ethanol, acetone.
Flammable solids
Flammable solids are materials that can easily ignite and spread fire quickly. They include substances that can undergo spontaneous combustion or are dangerous when wet.
Subdivisions:
- Cl.4.1: Flammable solids.
- Cl.4.2: Solids that can undergo spontaneous combustion.
- Cl.4.3: Solids that emit flammable gases when in contact with water.
Oxidizing substances and organic peroxides
Oxidizing substances can cause or intensify a fire by releasing oxygen, while organic peroxides are compounds that can be explosive and highly reactive.
Subdivisions:
- Cl.5.1: Oxidizing substances.
- Cl.5.2: Organic peroxides.
Toxic and infectious substances
These substances can cause serious harm to human health, whether by inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact.
Subdivisions:
- Cl.6.1: Toxic substances.
- Cl.6.2: Infectious substances.
Radioactive materials
Radioactive materials emit ionizing radiation, which can be dangerous to human health and the environment. They require extremely careful handling and storage.
Examples: Uranium, plutonium.
Corrosive substances
Corrosive substances can cause severe damage to living tissues and other materials through chemical reactions.
Examples: Sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide.
Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles
This category includes materials that do not fit into the other classes but still pose a significant risk.
Examples: Magnetized materials, environmentally hazardous substances.
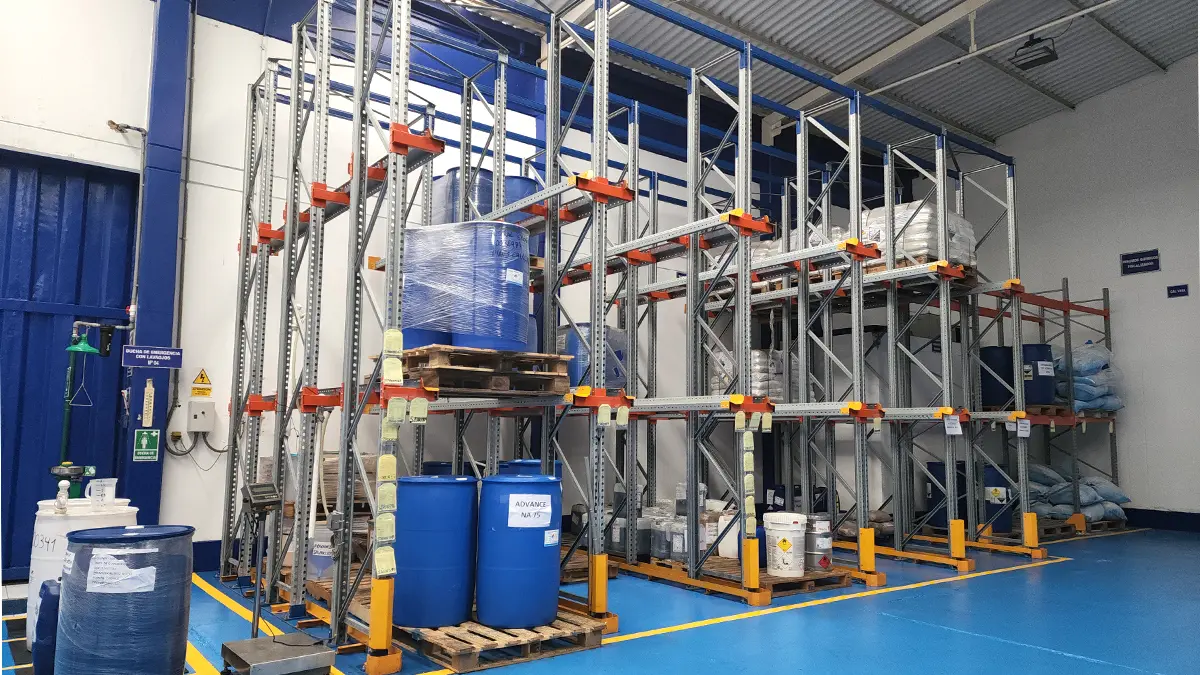

Characteristics and costs of storing hazardous materials
Storing hazardous materials involves additional costs due to strict safety and regulatory compliance requirements. Below are the main factors influencing these costs:
- Specialized infrastructure: Facilities must have advanced ventilation systems, spill containment, and segregated areas, significantly increasing construction and maintenance costs.
- Safety equipment: Investing in personal protective equipment, leak detection systems, and fire extinguishers is essential, representing a considerable expense.
- Staff training: Continuous training of staff in the safe handling of hazardous materials and emergency procedures is crucial and entails recurring costs.
- Insurance: Insurance premiums for facilities storing hazardous materials are higher due to the associated risks.
- Regulatory compliance: Companies must conduct regular audits, inspections, and updates to comply with local and international regulations, generating additional costs.
- Waste management: Safe and compliant disposal of hazardous waste is more expensive than non-hazardous waste disposal.
These factors increase storage costs but are essential to ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection. Investing in these areas not only prevents penalties but also improves the company's reputation and operational efficiency.
Regulations and standards in a hazardous materials warehouse
The storage of hazardous materials is regulated by various international and local standards. Some of the most relevant include:
- UN Dangerous Goods Regulations: Provides a global framework for the classification, packaging, labeling, and transportation of hazardous materials.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): In the United States, it establishes specific requirements for the safe storage of hazardous materials.
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association): Provides standards for the storage of flammable and combustible liquids.
- ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road): Regulates the transport and storage of hazardous goods in Europe.
Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid legal sanctions and ensure operational safety.
At AR Racking, we recommend studying each storage project on a case-by-case basis to ensure strict compliance with local regulations in each installation.
Signage in a hazardous materials warehouse
Signage in a hazardous waste warehouse is a fundamental element to ensure safety, prevent accidents, and comply with current regulations. Proper identification of areas and stored materials facilitates operational management and reduces the risk of incidents.
In a warehouse of this type of substances, the following types of signage should be considered and included:
Waste labelling
Each container must have a clear and visible label indicating the nature of the stored waste. The Globally Harmonized System (GHS) establishes the hazard pictograms that must be included to inform about risks such as flammability, toxicity, or reactivity.
Storage area delimitation
It is essential to differentiate storage areas according to the type of waste, avoiding incompatible mixtures that could generate dangerous reactions. For this, the use of colours, floor lines, and signs clearly indicating the classification of the waste is recommended.
Evacuation and emergency route signage
All warehouses must have well-defined evacuation routes, signposted with visible and weather-resistant signs. It is also essential to indicate the location of assembly points and emergency response equipment, such as decontamination showers, fire extinguishers, and spill containment kits.
Indications for the use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
In each area of the warehouse, signage must be installed indicating which personal protective equipment is mandatory. This may include gloves, goggles, masks, or special suits, depending on the hazard of the stored waste.
Signage for containment and spill management areas
Hazardous waste warehouses must have designated areas for leak and spill containment. Signage must clearly indicate the location of absorbents, containment barriers, and emergency containers to minimise environmental impact and prevent the spread of hazardous material.
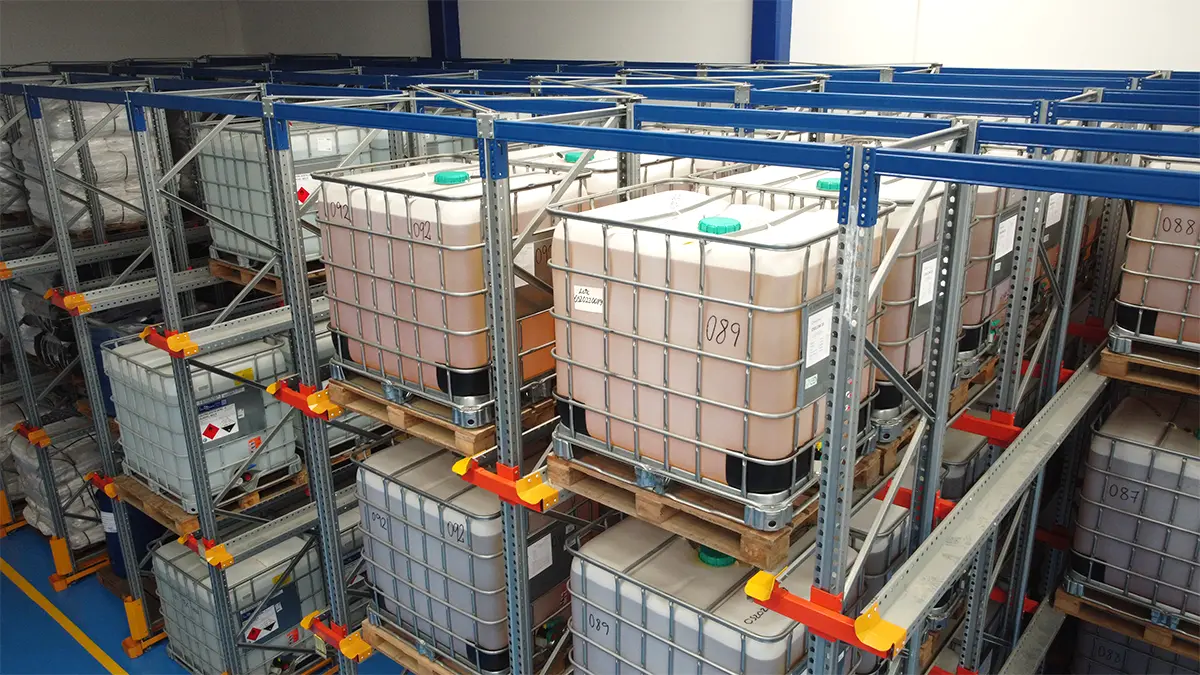

Best practices for storage
To store hazardous materials safely, it is important to follow a series of best practices:
- Proper identification and labelling: All hazardous materials must be labelled with information about their risks and safety measures.
- Separation and segregated storage: Incompatible materials must be stored separately to avoid dangerous reactions.
- Use of appropriate containers and receptacles: Use containers that are resistant to the stored materials and comply with safety regulations.
- Ventilation and temperature control systems: Ensure adequate ventilation and safe temperatures for the materials to prevent fires or explosions.
- Protective equipment and safety measures: Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) and establish safety procedures for handling hazardous materials.
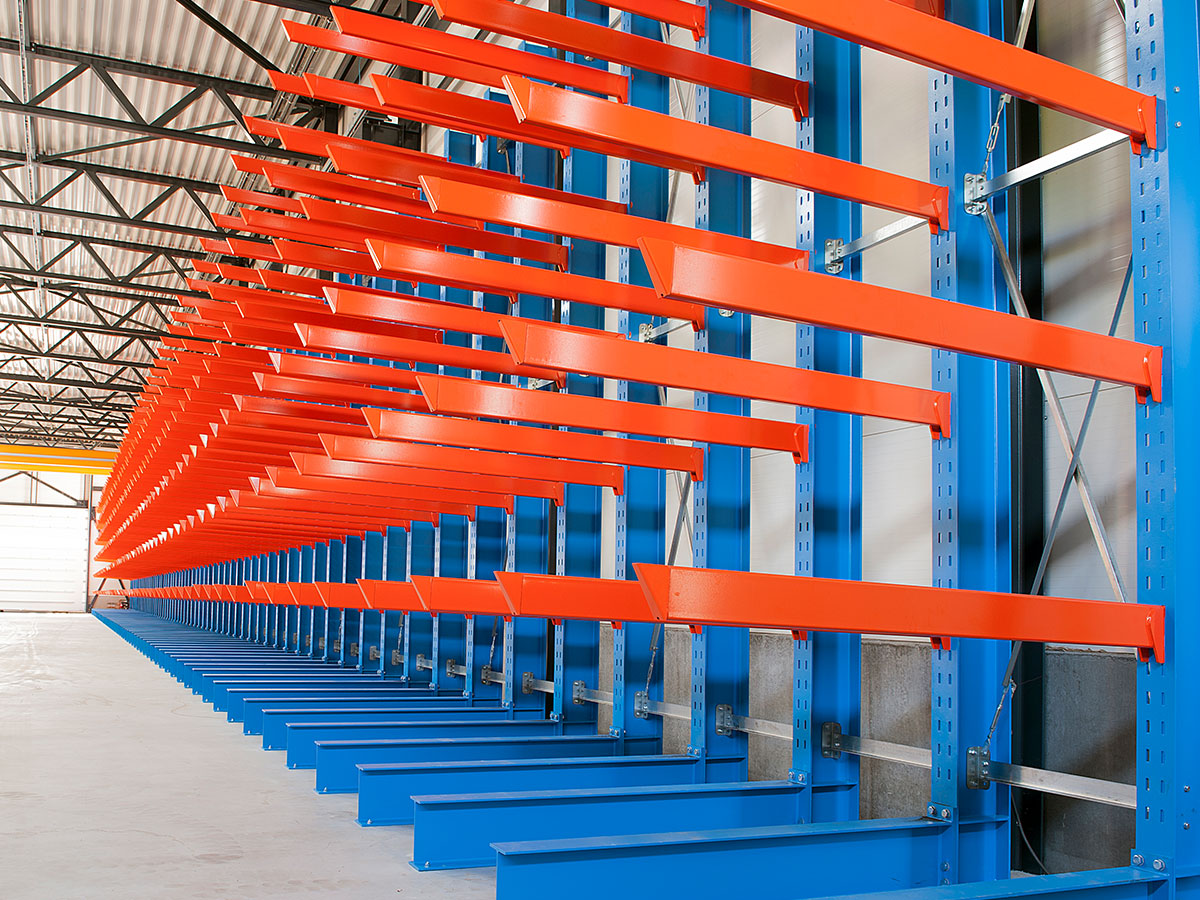
Special racking systems for hazardous materials
The use of specialised racking systems is essential for the safe storage of hazardous materials. AR Racking offers a variety of solutions specifically designed for this purpose:
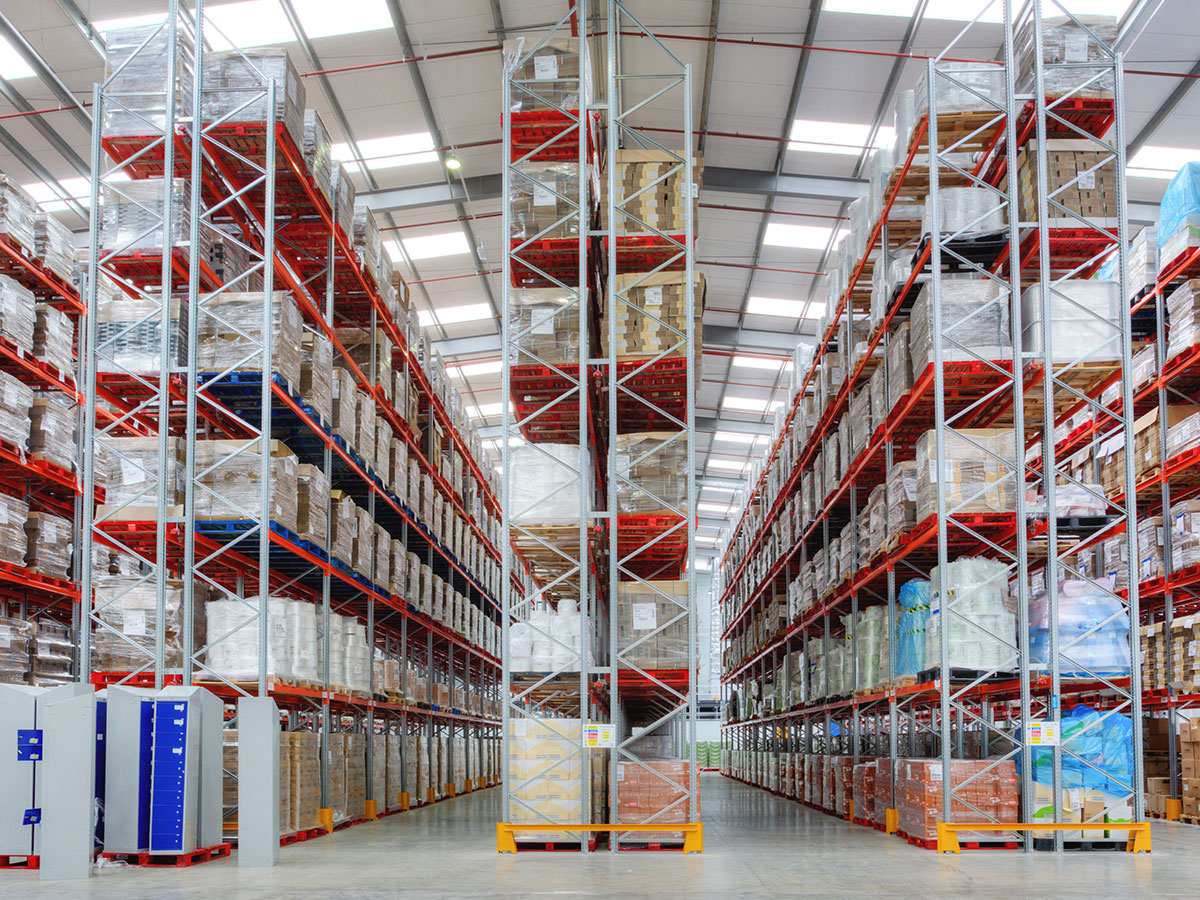
Adjustable Pallet Racking
These racking systems are designed to store pallets safely and efficiently. They are ideal for hazardous materials stored in large containers or drums. Made of high-strength steel, these racking systems can withstand heavy loads and are designed to resist corrosion and wear.
Live Storage Pallet Racking (FIFO)
These systems use rollers or conveyors to facilitate the movement of materials within the warehouse. They are ideal for hazardous materials that require frequent rotation. These racking systems improve storage efficiency and reduce the risk of accidents by minimising manual handling of materials.
Sustainability
To store hazardous goods sustainably, companies can adopt practices such as using recyclable and reusable materials, implementing energy-efficient systems, properly managing waste, using monitoring technologies, training staff in sustainability, integrating renewable energy, designing eco-friendly warehouses, optimising transport to reduce emissions, adopting environmental management systems like ISO 14001, and collaborating with sustainable suppliers.
These tips not only protect the environment but also improve operational efficiency and the company's reputation.
Conclusion
Safe storage of hazardous materials is a critical responsibility for any company handling these substances. By following best practices and complying with current regulations, it is possible to minimise risks and protect human health, the environment, and facilities.
Investing in specialised racking systems from AR Racking and staff training are essential steps to achieve safe and efficient storage. Contact us for personalised advice to operate your warehouse safely and efficiently.